Reflection and refraction in 2D and 3D
Reflection in 2D
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import math
from torchlensmaker.core.rot2d import rot2d
from torchlensmaker.core.physics import reflection
from torchlensmaker.testing.basic_transform import basic_transform
def plotv(v, **kwargs):
plt.plot([0, v[0]], [0, v[1]], **kwargs)
def demo_reflection(theta_i: float, normal_angle: float) -> None:
"""
theta_i: incident angle
normal_angle: angle of the vector normal to the surface
"""
# surface normal vector
normal = rot2d(torch.tensor([1., 0.]), normal_angle)
B = 10
# Make some random incident rays around theta_i
all_theta_i = torch.full((B,), theta_i) + torch.deg2rad(torch.tensor(20.))*torch.rand(B)
V = torch.zeros(B, 2)
for i in range(B):
V[i] = torch.as_tensor(-rot2d(normal, all_theta_i[i]), dtype=torch.float32)
# Use the same normal for all incident rays
all_normal = torch.tile(torch.as_tensor(normal, dtype=torch.float32), (B, 1))
# Sanity checks
assert(torch.allclose(torch.linalg.norm(V, axis=1), torch.tensor(1.0)))
assert(torch.allclose(torch.linalg.norm(all_normal, axis=1), torch.tensor(1.0)))
assert( torch.allclose(torch.sum(-V * all_normal, dim=1), torch.cos(all_theta_i)) )
reflected = reflection(V, normal)
# Verify using the trigonometric version of reflection
theta_r = torch.arctan2(reflected[:, 1], reflected[:, 0]) - torch.arctan2(all_normal[:, 1], all_normal[:, 0])
assert torch.allclose(theta_r, -all_theta_i)
assert(torch.allclose(torch.linalg.norm(reflected, axis=1), torch.tensor(1.0)))
# Rendering
# Draw the surface
plotv(rot2d(normal, math.pi/2), color="lightblue")
plotv(rot2d(normal, -math.pi/2), color="lightblue")
# Draw the normal
plotv(normal, linestyle="--", color="grey")
for i in range(B):
# Draw incident light ray
plotv(-V[i], color="orange")
# Draw reflected light ray
plotv(reflected[i], color="red")
plt.gca().set_xlim([-1, 1])
plt.gca().set_ylim([-1, 1])
plt.gca().set_title("Reflection")
plt.gca().set_aspect("equal")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
demo_reflection(theta_i = torch.deg2rad(torch.tensor(12.16)), normal_angle=torch.deg2rad(torch.tensor(105.0)))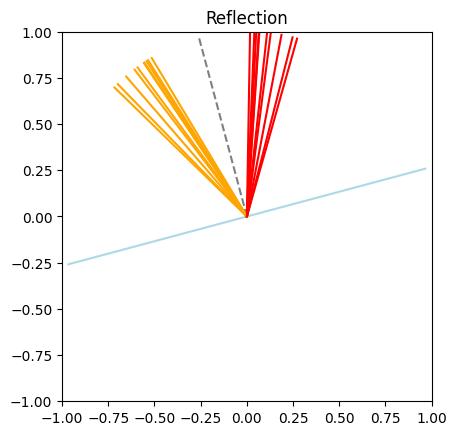
Refraction in 2D
python
import math
import torch
from torchlensmaker.core.physics import refraction
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
import numpy as np
from IPython.display import display, HTML
def plotv(v, **kwargs):
plt.plot([0, v[0]], [0, v[1]], **kwargs)
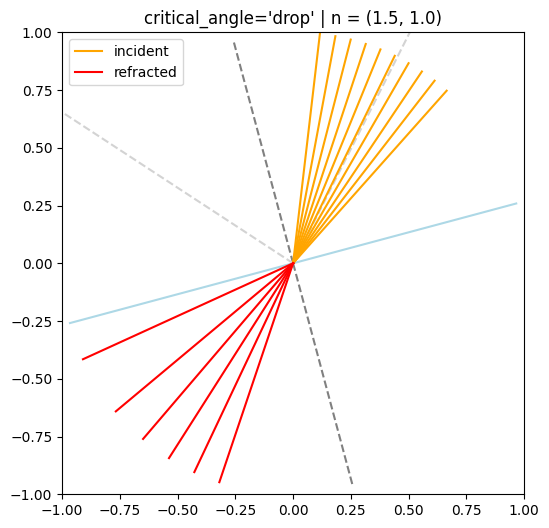
def demo_batched_refraction(crit_option, theta_i: float, normal_angle: float, n1, n2):
"""
Demo / Test of a batched refraction function
theta_i: incident angle
normal_angle: angle of the vector normal to the surface
"""
# Critical angle
if n1 > n2:
critical_angle = np.arcsin(n2/n1, dtype=np.float32)
print("Critical angle: {:.2f} deg".format(np.degrees(np.arcsin(n2/n1), dtype=np.float32)))
else:
critical_angle = None
print("No critical angle")
# Surface normal vector
normal = rot2d(torch.tensor([1., 0.]), normal_angle)
B = 10
# Make B incident rays +- 20 deg around theta_i
spread = np.radians(35)
noise = torch.linspace(-spread/2, spread/2, B)
all_theta_i = torch.full((B,), theta_i) + noise
V = torch.zeros(B, 2)
for i in range(B):
V[i] = torch.as_tensor(-rot2d(normal, all_theta_i[i]), dtype=torch.float32)
# Use the same normal for all incident rays
all_normal = torch.tile(torch.as_tensor(normal, dtype=torch.float32), (B, 1))
# Sanity checks
assert(np.allclose(np.linalg.norm(V, axis=1), 1.0))
assert(np.allclose(np.linalg.norm(all_normal, axis=1), 1.0))
assert( torch.allclose(torch.sum(-V * all_normal, dim=1), torch.cos(all_theta_i)) )
# Call refraction function
refracted, _ = refraction(V, all_normal, n1, n2, critical_angle=crit_option)
# Check for nans
number_of_nonfinite = (~torch.isfinite(refracted).any(dim=1)).sum()
if number_of_nonfinite > 0:
print(f"Warning! {number_of_nonfinite} refracted rays contain nan!")
if V.shape[0] != refracted.shape[0]:
print(f"Warning! {V.shape[0]} incident rays but only {refracted.shape[0]} refracted rays.")
# Rendering
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 6))
# Draw the surface
plotv(rot2d(normal, math.pi/2), color="lightblue")
plotv(rot2d(normal, -math.pi/2), color="lightblue")
# Draw the normal
plotv(normal, linestyle="--", color="grey")
plotv(-normal, linestyle="--", color="grey")
# Draw critical angle line
if critical_angle is not None:
plotv(1.5*rot2d(normal, critical_angle), linestyle="--", color="lightgrey")
plotv(1.5*rot2d(normal, -critical_angle), linestyle="--", color="lightgrey")
# Draw incident and refracted light rays
for i in range(V.shape[0]):
plotv(-V[i], color="orange")
for i in range(refracted.shape[0]):
plotv(refracted[i], color="red")
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-1, 1])
title = f"critical_angle='{crit_option}' | n = ({n1}, {n2})"
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
orange_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='orange', label='incident')
red_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='red', label='refracted')
ax.legend(handles=[orange_line, red_line])
display(fig)
plt.close(fig)
crit_options = [
'nan',
'clamp',
'drop',
]
plt.ioff()
theta_i = np.radians(-39.16, dtype=np.float32)
normal_angle=np.radians(105, dtype=np.float32)
n1, n2 = 1.5, 1.0
for c in crit_options:
demo_batched_refraction(c, theta_i, normal_angle, n1, n2)
display(HTML("<hr>"))Critical angle: 41.81 deg
Warning! 4 refracted rays contain nan!
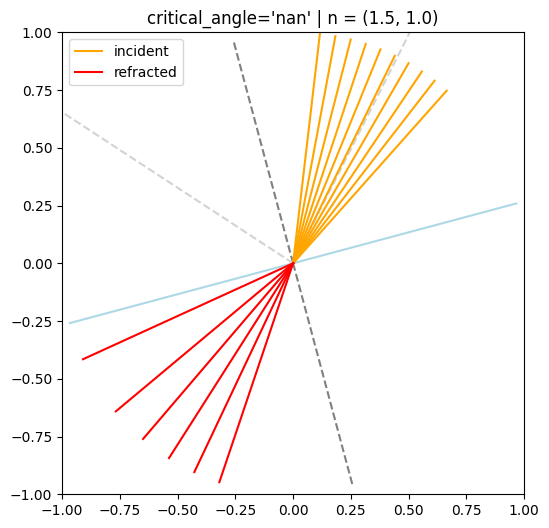
Critical angle: 41.81 deg
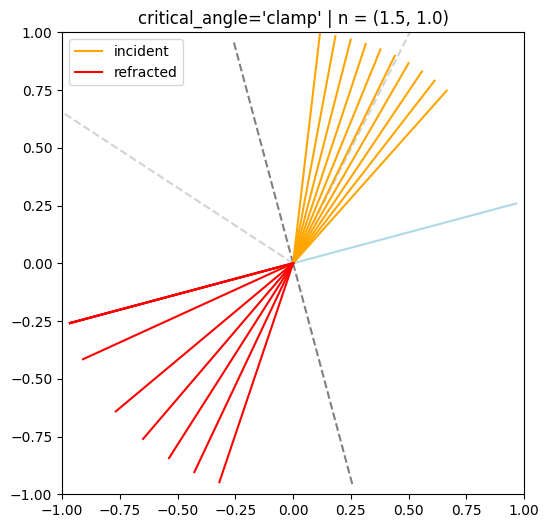
Critical angle: 41.81 deg
Warning! 10 incident rays but only 6 refracted rays.
Common setup for 3D demo
python
import torch
import torchlensmaker as tlm
def deg(x):
return torch.deg2rad(torch.as_tensor(x))
def make_incident_vectors(a, b, alpha_n, beta_n):
beta_range = torch.linspace(0, torch.deg2rad(torch.as_tensor(25.0)), beta_n)
alpha_range = torch.linspace(-torch.pi, torch.pi, alpha_n)
alpha, beta = map(
lambda t: t.reshape(-1), torch.meshgrid(alpha_range, beta_range, indexing="xy")
)
x = torch.sin(beta) * torch.cos(alpha)
y = torch.sin(beta) * torch.sin(alpha)
z = torch.cos(beta)
Rb = torch.tensor(
[[1, 0, 0], [0, torch.cos(b), -torch.sin(b)], [0, torch.sin(b), torch.cos(b)]]
)
Ra = torch.tensor(
[[torch.cos(a), 0, torch.sin(a)], [0, 1, 0], [-torch.sin(a), 0, torch.cos(a)]]
)
R = torch.mm(Rb, Ra)
return -torch.mm(torch.column_stack((x, y, z)), R.T)
def demo_light(a, b, alpha_n, beta_n, function):
# incident rays unit vectors
incident = make_incident_vectors(a, b, alpha_n, beta_n)
# colliding with the X=0 plane
normals = torch.tensor([-1, 0, 0]).expand_as(incident)
# compute reflection / refraction
outcident = function(incident, normals)
if isinstance(outcident, tuple):
outcident = outcident[0]
# verity unit norm
assert torch.all(torch.le(torch.abs(torch.linalg.norm(outcident, dim=1) - 1.0), 1e-5))
surface = tlm.SquarePlane(2.)
transform = basic_transform(1.0, "origin", [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0])(surface)
# rays to display vectors
incident_display = torch.column_stack((torch.zeros_like(incident), -incident))
outcident_display = torch.column_stack((torch.zeros_like(outcident), outcident))
scene = tlm.viewer.new_scene("3D")
scene["data"].append(tlm.viewer.render_surfaces([surface], [transform], dim=3))
scene["data"].append(tlm.viewer.render_rays(
incident_display[:, :3],
incident_display[:, :3] + 1 * incident_display[:, 3:6],
default_color="orange", layer=0))
scene["data"].append(tlm.viewer.render_rays(outcident_display[:, :3],
outcident_display[:, :3] + 1 * outcident_display[:, 3:6],
default_color="red", layer=0))
tlm.viewer.display_scene(scene)Reflection in 3D
python
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 1, 1, tlm.reflection)
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 1, 30, tlm.reflection)
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 30, 30, tlm.reflection)Refraction in 3D
python
# A single ray entering a denser medium
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 1, 1, lambda rays, normals: tlm.refraction(rays, normals, n1=1.0, n2=1.5))python
# a 2D cone of 3D rays entering glass
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 1, 30, lambda rays, normals: tlm.refraction(rays, normals, n1=1.0, n2=1.5))python
# a 3D cone of rays entering diamond
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-50), 30, 30, lambda rays, normals: tlm.refraction(rays, normals, n1=1.0, n2=2.417))python
# 3D cone of rays exiting from glass to air
# some rays are beyond the critical angle
demo_light(deg(-30), deg(-20), 30, 30, lambda rays, normals: tlm.refraction(rays, normals, n1=1.5, n2=1.0, critical_angle="drop"))python
# 3D cone of rays exiting from diamond to air
# with total internal reflection
demo_light(deg(-60), deg(-20), 30, 20, lambda rays, normals: tlm.refraction(rays, normals, n1=2.417, n2=1.0, critical_angle="reflect"))